PV module lamination is a key step in solar panel manufacturing, as it affects the longevity, reliability, and performance of the module. In this complete guide, we will explore what PV module lamination is, what its benefits are, and what the process of laminating PV modules looks like.
What Is PV Module Lamination?
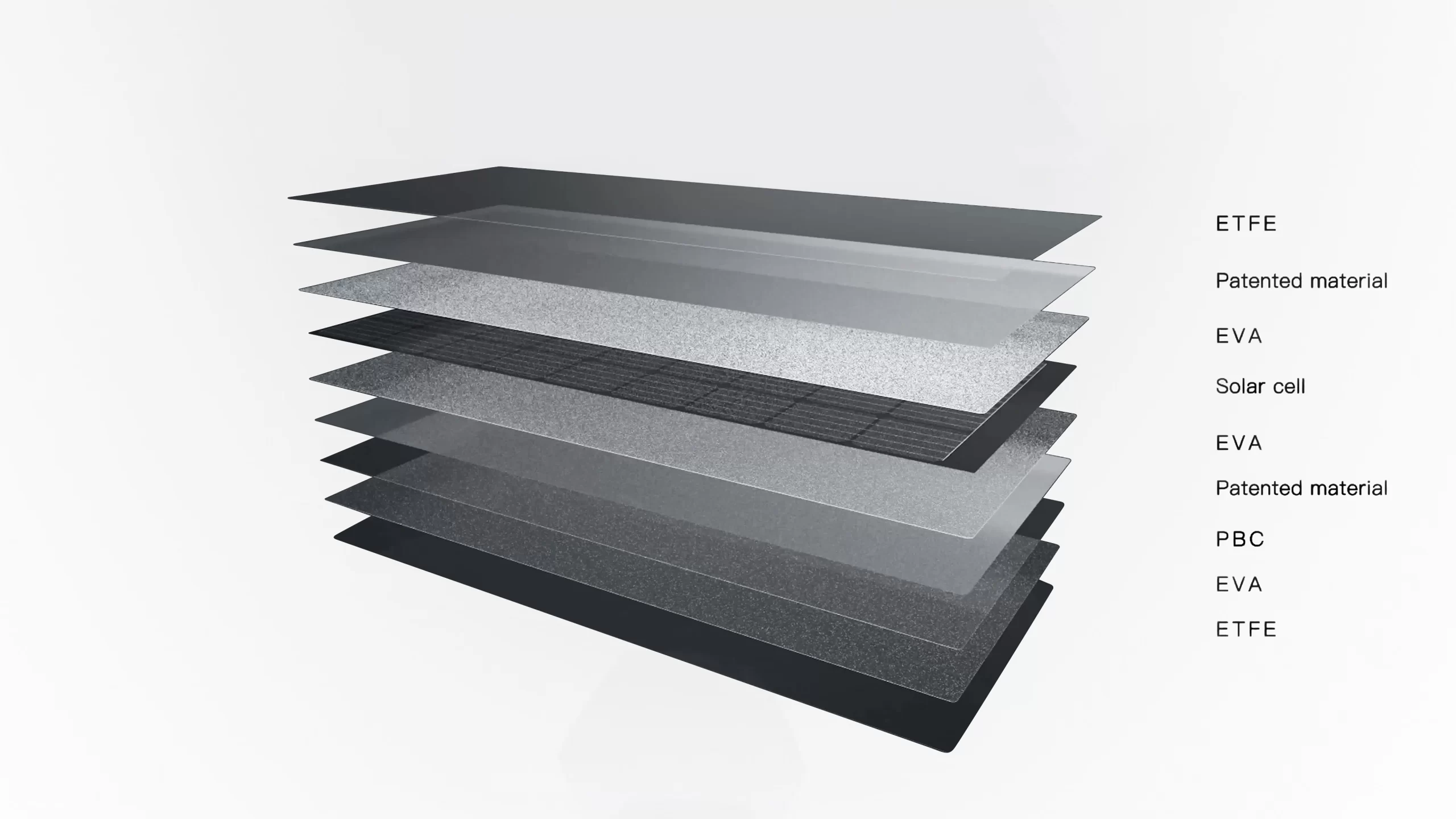
PV module lamination is a process that seals the solar cells between layers of protective materials, such as glass, ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), and tedlar polyester tedlar (TPT). The purpose of PV module lamination is to protect the solar cells from environmental factors, such as moisture, dust, and temperature changes, and to ensure the durability and performance of the module. The most common way to laminate a PV module is by using a lamination machine, which applies heat and pressure to the module in a vacuum chamber.
This process causes the EVA to melt and bond with the glass and TPT, forming a solid laminate. The lamination machine can also remove air bubbles and impurities from the module, improving its quality and efficiency.

The Benefits of PV Module Lamination
Sungold engineers said the PV module lamination process makes solar panels more durable and reliable. And why is PV module lamination so important?
PV module lamination is designed to stabilize the core components of a solar module to increase its reliability and extend its life. In this process, critical components are tightly bonded together to give higher performance and longer life to the final product.
Once laminated, reworking and remanufacturing becomes extremely difficult. Therefore, it becomes a crucial step to ensure the performance and safety of the components and reduce the scrap rate through rigorous visual inspection and electroluminescence inspection, i.e. EL testing & EL inspection, before lamination. Such upfront quality control measures help safeguard the quality of the final product so that it can demonstrate superior reliability and durability in real-world applications.
Process of PV Module Lamination
-PV module lamination increases the durability of solar panels.
By encapsulating the solar cells and connections within a protective material, the panel is shielded from the elements and is less likely to be damaged by environmental factors such as moisture, temperature changes, and physical impact. This increased durability allows solar panels to last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements and saving on costs in the long run.
-PV module lamination increased the efficiency of solar panels.
The protective layer used in lamination is typically made of ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), a material that has been shown to improve the efficiency of solar panels by up to 2%. This increase in efficiency is due to the reduction in reflection and the improved ability of the cells to absorb light.
-Additionally, the use of EVA in the lamination process provides insulation, which helps to maintain a consistent temperature within the solar panel.
This insulation can prevent hotspots, which are areas of the panel that can become overheated and reduce the efficiency of the cells. By reducing hotspots, PV module lamination further improves the overall efficiency of solar panels.
What Is the Process of PV Module Lamination?
The process of PV module lamination typically involves the use of a laminator machine. The solar cells and connecting wires are arranged in a specific pattern and placed between two layers of EVA film. This assembly is then passed through the laminator, which applies heat and pressure to fuse the layers, creating a solid and durable panel.
Once the panel has been laminated, it can be tested for quality and efficiency. These tests may include checking the electrical output, visual inspection for defects, and measuring the thickness and uniformity of the EVA layer.
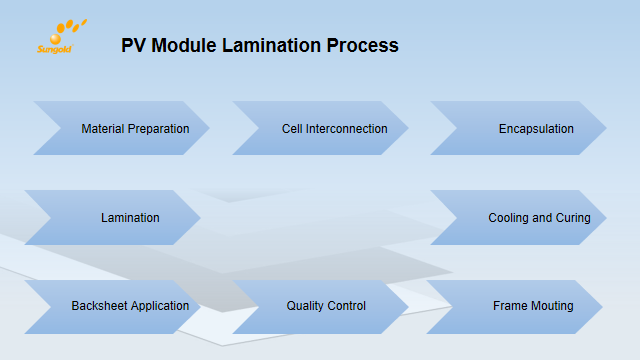
Step#1:Material Preparation
The lamination process begins with the preparation of the necessary materials, including the solar cells, the encapsulation sheet (usually made of ethylene vinyl acetate or EVA), tempered glass, and the back sheet.
Step#2:Cell Interconnection
Solar cells are interconnected to form solar modules. These cells are typically arranged in a specific pattern to optimize the power output of the panel.
Step#3:Encapsulation
A layer of encapsulant (EVA) is placed between the interconnected solar cells and the tempered glass cover. This layer acts as an adhesive to bond the cells to the glass and protects them from moisture and environmental factors.
Step#4:Lamination
The assembled solar cells, encapsulation material, and glass layers are placed in a vacuum laminator. The machine heats the encapsulating material, creating a vacuum to remove air bubbles trapped between the layers. This process ensures that the layers are firmly bonded together.
Step#5:Cooling and Curing
After lamination, the module is cooled to cure the encapsulant, effectively sealing the solar cell within the protective layer. This curing process ensures the durability and longevity of the encapsulation.
Step#6:Backsheet Application
Backsheets provide additional protection for the backside of the solar panel and are used after lamination. Backsheets are usually made of materials that are resistant to moisture and UV radiation.
Step#6:Quality Control
Laminated modules are subjected to quality control tests to check for defects such as bubbles, delamination, or electrical problems. These tests ensure that the panels meet industry standards and perform reliably over their lifetime.
Step#7:FRAME MOUNTING
In some cases, a metal frame is mounted around the edge of the solar panel to provide further protection and ease of installation.
Common Issues and Solutions in Lamination
Despite careful processing, issues may arise during lamination, including:
- Bubbles: Entrapped air bubbles can affect module performance. Solutions include vacuuming or adjusting lamination parameters.
- Uneven Pressure: Inconsistent pressure distribution during lamination may lead to uneven encapsulation. Proper alignment and calibration of laminating equipment can address this issue.
Future Trends in Layering Technology
The future of PV module lamination is marked by advancements in materials and automation:
- New Encapsulant Materials: Research continues to develop encapsulant materials with enhanced durability, UV resistance, and efficiency.
- Automation and Robotics: Increasing automation in lamination processes improves efficiency, reduces costs, and ensures consistent quality.
FAQs
What is the lamination process of the PV module?
Lamination seals solar cells between protective layers, enhancing durability and performance.
What is PV laminate?
PV laminate is a multilayer structure providing electrical insulation and protection for solar cells.
Why does delamination occur in PV cells?
Delamination can result from poor-quality materials, improper processes, thermal stress, moisture, or mechanical damage.
What is the process of laminating?
Laminating involves applying a thin film to materials to enhance their appearance and durability.
How long is the lamination process?
The duration varies but typically takes a few minutes per sheet, depending on material and equipment.
What is the difference between lamination and encapsulation?
Lamination uses a thin film for protection, while encapsulation uses a thicker film, providing more durability and sealing the edges.
PV module lamination is an essential process in the PV module manufacturing process. It provides numerous benefits, including increased durability and efficiency, which make solar energy a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly option. By understanding the benefits and process of PV module lamination, we can better appreciate the technology behind this innovative energy source and its potential to transform the way we power our world. You can also click Sungold Solar to learn more about concerning information about solar panels.