What are solar panel wires?
Solar cable is basically a wire or cable used in solar panels to withstand the high temperatures of the sun during the energy accumulation process. Ordinary cables and wires cannot withstand high voltage and current, it requires large-capacity wires. Solar cables are very useful not only in solar panels and solar power plants, but also in your home appliances and more.

How are solar panel wires classified?
Solar panel wires can generally be classified based on their function and purpose. Here are some common classification methods:
Direct current (DC) wires and alternating current (AC) wires:
DC Wire: The wire that connects the solar panel to the charge controller is usually a DC wire because the current generated by the solar panel is DC.
AC Wires: The wires that connect the inverter to the grid are usually AC wires because the inverter converts DC power into AC power for use in your home or network.
Voltage level:Low Voltage Wire: Typically used for solar panel to charge controller connections and has lower voltage.
High-voltage wires: usually used to connect the inverter to the grid, with higher voltages.
Wire size:Wire sizes can be classified according to the current capacity and voltage reduction required. Larger wires are typically used to handle higher current loads.
Solar cable types:Solar cables are often classified according to their special design and insulation materials to suit outdoor and high-temperature environments.
Solar cables are often classified according to their special design and insulation materials to suit outdoor and high-temperature environments.
Solar panel wires classified by color
The color classification of solar panel wires usually follows international standards to ensure reliability and consistency in installation and maintenance. Here is a common classification of solar panel wire colors:
Red: Usually indicates the positive wire, which is the positive direction of current. The red wire connects to the positive terminal of the solar panel.
Black: Usually indicates the negative wire, which is the negative direction of current. The black wire connects to the negative terminal of the solar panel.
Blue: Sometimes blue wires are used to represent connections between panels, or to connect groups of panels in series. This can help differentiate between the connections between the panels and the connections between the panels and the inverter.
Green or Green/Yellow: This usually indicates a ground wire, which is used to ensure the safety of the system to prevent electric shock hazards. In some areas this may be green, while in others it may be green and yellow.
solar panel cable by thickness
The thickness of solar panel cable is usually determined by the gauge and material of the wire, rather than its color. Wires used in solar panel systems typically come in the following common specifications:
10 AWG (American Wire Gauge): This is a thicker wire usually used to connect between solar panels and inverters to withstand larger current loads.
12 AWG: This is a medium gauge wire that is also commonly used for internal connections in solar panel systems and for connecting panels in series.
14 AWG: This is a thinner wire typically used in low-current circuits, such as wires for connections inside solar panels or auxiliary equipment.
16 AWG or smaller: Thinner wire may be used for low power or low current applications such as sensors, monitoring systems, etc.

Solar panel wires classified by length
Solar panel wire lengths often vary based on specific solar system layout and needs, so there is no specific standard length classification. Wire length will vary based on the following factors:
Mounting location and layout: The mounting location and layout of your solar panels will affect the length of the wires. For example, solar panels mounted on a roof may require longer wires, while ground-mounted or solar tracking systems may require shorter wires.
Distance between panels: The distance between panels also affects the length of the wires. If the panels are further apart, the wires connecting them may be longer.
Wire Path: Wires must run from the solar panels to the inverter or battery system, so the path of the wire also affects its length. If the wires have to travel long distances, they may be longer.
System Design: System design requirements will also affect the length of the wires. For example, some systems may require panels to be connected in series, which may require more wire length.
Types of Solar Panel Wires
The type of wire used in a solar panel system is usually chosen based on its purpose and environmental conditions. Here are some common solar panel wire types:
DC Wires: These wires are used to connect the circuit between the solar panel and the inverter to convert the DC power generated by the solar panel into AC power. DC wires are usually labeled positive (+) and negative (-) to distinguish polarity.
AC Wires: Once the inverter converts the current generated by the solar panels into AC power, AC wires are used to deliver the power to the home grid or power network. These wires typically use standard electrical wires such as THWN or THHN wire.
Solar PV Cable: Solar cable is a wire specially designed for solar systems and is resistant to UV radiation, high temperature and abrasion. They usually come with a sun protection sheath to ensure protection from damage during extended use in outdoor environments.
Grounding Wire: Grounding wires are used to ground solar panels and solar cell systems to the ground to provide safety and reduce the risk of electric shock. These wires are usually green or green and yellow and meet grounding standards.
Communication Wires: In some systems, communication wires are used to connect communications between solar panels and inverters to monitor and manage system performance.
Monitoring Wires: Wires used for system monitoring and data collection to track solar panel and system performance.
Comparison of all solar panel wire types
The types of wires used in solar panel systems vary in function and purpose. Here’s a comparison of various solar panel wire types:
DC wires vs. AC wires:
DC wires are used between solar panels and inverters to carry the DC power generated by the solar panels. These wires typically require larger cross-sectional areas to handle higher currents.
AC wires are used to connect the AC power generated by the inverter to the home grid or power network. They usually use standard electrical wires and have a smaller cross-section because the inverter converts the current to a lower current level.
Solar cables vs. communication wires vs. monitoring wires:
Solar cables are wires specifically designed for use in solar systems with sun protection jacketing and durability. They are used to connect solar panels and inverters and are used in outdoor environments for extended periods of time.
Communication wires are used for communication between system components to monitor and manage the solar panel system. They may include data lines and control lines.
Monitoring wires are used to connect sensors and monitoring equipment to track system performance and detect problems.
Ground Wire: Ground wires are used to connect solar panels and solar battery systems to the ground to provide safety and reduce the risk of electric shock. They are usually green or green and yellow and meet grounding standards.
How to choose the right solar panel wire size?
Choosing the right solar panel wire size is an important step in ensuring the safety and performance of your solar system. The following are key factors in selecting wire size:
Current Load: First, you need to determine the maximum current load that your solar panel will produce. This is usually determined by the current rating and number of solar panels. The cross-sectional area (conductor size) of the wire is selected to be able to withstand this current to prevent overheating of the wire and loss of power. Generally, larger current loads require larger cross-sectional area wires.
Resistance and Power Loss: Smaller cross-sectional area wires result in greater resistance, resulting in additional power loss. Therefore, to minimize power loss, choose wires that are large enough to reduce resistance.
Wire Length: Wire length is also an important factor in choosing wire size. The longer the wire, the greater the resistance, so a larger cross-sectional area of wire is required to reduce power loss.
Environmental conditions: Consider the environment in which the solar panel system will be installed. If the wires need to operate in high or low temperatures, or need to be exposed to UV rays, then you need to choose wires that are resistant to high temperatures, low temperatures, and UV radiation.
Electrical Standards: Make sure the wire you choose complies with your area’s electrical standards and regulations. This includes the wire’s insulation properties, wear resistance, fire resistance, etc.
Safety: Consider safety when choosing wires. The electrical wiring of your solar panel system should be durable enough to prevent electrical failures and fire risks. Wires should have appropriate insulation to prevent electric shock hazards.
Manufacturer Recommendations: Follow the recommendations of the solar panel and inverter manufacturers, they will usually provide guidance on the required wire size.
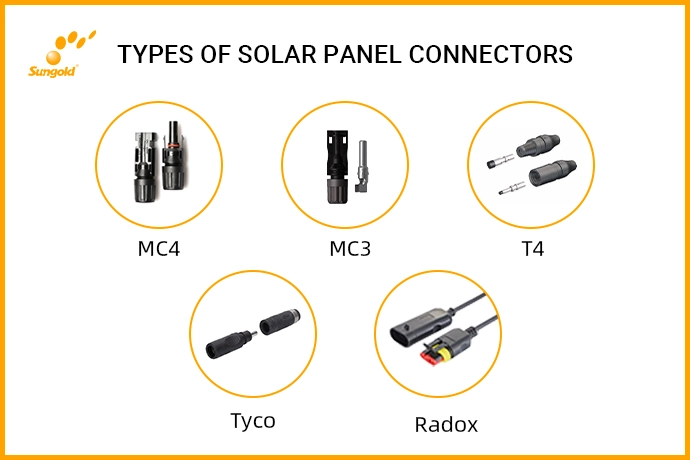
What type of connectors are used for solar panels?
MC4: Industry Standard
MC4 is currently the industry standard for solar panel systems, providing a reliable and secure connection between solar panels and other components of the photovoltaic system. They are weatherproof, UV resistant and durable in harsh weather. They ensure a stable connection throughout the life of the solar array.
There are male and female versions, both of which make the correct connection while avoiding reverse polarity. They have a simple push-and-lock mechanism that provides a secure connection, reducing the risk of accidental disconnection.
MC4 is by far the most popular type due to its safety, reliability and compatibility with various solar modules.
MC3: An obsolete technology
MC3 is an older generation solar panel connector. They used to be popular, but MC4 has largely replaced them. They feature a snap-on locking mechanism that is less secure than the MC4 locking system.
MC3 also tends to be less weather-resistant and is more susceptible to corrosion and wear over time. While they still exist in some PV installations, MC3 has become less common due to the superior performance, safety and reliability of MC4.
If you have a system that is over ten years old, it may be time to check out the connectors and upgrade them to MC4s.
T4 connector
The T4 connector is another type of solar panel connector developed by Amphenol Industrial Solar Technologies. As replacements for MC4, they have some improvements in security and ease of use.
T4 connectors have a threadless design, allowing for quick and easy installation and disconnection. They require no specialized tools. T4 also has higher current carrying capacity and better durability compared to MC4.
While T4 connectors are becoming increasingly popular in PV installations, they have not seen the same widespread adoption as MC4 connectors, which remain the industry’s mainstream choice.

Solar Panel Wires FAQs
What special meaning does the color of the wire have?
Solar panel wires colors usually follow international standards to ensure consistency and safety. Typically, a red wire represents the positive terminal, a black wire represents the negative terminal, and a green or green-and-yellow wire represents the ground wire. Other colors may be used to distinguish different circuits or functions.
How to choose olar panel wires size?
The choice of wire size depends on the current load of the solar panel system, wire length, environmental conditions and safety requirements. Generally speaking, wires with a large enough cross-sectional area should be selected to meet the current demand and reduce power loss. A professional solar installer or electrical engineer can provide advice.
How durable does the wire need to be?
Solar panel wires should be durable enough to withstand UV rays, high temperatures, low temperatures, and physical damage found in outdoor environments. Solar cables often have these properties and are capable of being used in outdoor environments for extended periods of time.
How do the wires connect to the solar panels and inverter?
Wires are usually connected to the solar panel through cable connectors and then to the inverter through connectors or terminals. These connections should be made in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations and installation guidelines to ensure they are tight, safe and secure.
What should I pay attention to when installing wires?
Wire installation should comply with applicable electrical codes and regulations. Wires should be properly secured and protected to prevent damage and electrical failure. Regularly inspect and maintain electrical wiring connections to ensure system stability and performance.
Why is a ground wire needed?
Ground wires are used to connect solar panels and solar battery systems to the ground to provide safety and reduce the risk of electric shock. This helps direct potential voltage differences to ground to protect personnel and equipment.
What is the lifespan of a wire?
The lifespan of a wire depends on a variety of factors, including material quality, installation quality, environmental conditions and usage. Generally, solar cables have a long lifespan and can be used in solar systems for many years.
Are there any special safety precautions?
When handling solar panel wires, always use caution to ensure power is disconnected and appropriate safety measures are taken to avoid shock hazards. Electrical wiring should be installed and maintained under the guidance of professionals and in compliance with safety regulations.
How to detect wire faults?
Wire faults may include broken wires, short circuits, or connection issues. Detecting electrical wiring faults often requires the use of electronic test equipment, such as multi-purpose electric meters. If you suspect there is a problem with the electrical wiring, contact a professional immediately for repair.










